Filament Under Control: Smart Tips to Get the Most Out of Your 3D Printer
3D filament is the heart of every 3D print. Every meter wasted means money — and creativity — going down the drain. The good news? There are plenty of ways to optimize filament usage, reduce leftover material, and maintain print quality at the same time. With a few smart habits, you can save money, be more sustainable, and make your 3D printer work at its best.
Whether you’re a beginner maker, a 3D artist, or a small business owner selling printed products, this guide will help you turn leftover filament into opportunities — while preventing issues caused by humidity and improper storage.
Why 3D Filament Matters (and Why It’s So Expensive)
Your 3D filament isn’t just a roll of plastic — it’s a core investment that represents your time, energy, and creativity. It’s the foundation of your projects: without quality filament, no printer can deliver reliable results. But as the number of available materials, colors, and types grows (PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU, and more), disorganized usage often leads to waste.
According to data from 3D Printing Industry, small creators waste an average of 20% of the 3D filament they buy due to calibration tests, color changes, or print errors. That means for every 10 kg of filament, around 2 kg ends up unused — a loss that can easily be avoided with better planning.
In this guide, you’ll learn practical ways to get the most out of your 3D filament, from creative reuse to humidity control and sustainable storage solutions.
1. Use Color Changes for Test Prints or Freebies
During a color swap or at the end of a spool, many users simply cut the 3D filament and discard the remainder. Instead, use those small leftovers for printing test pieces, calibration cubes, or small trinkets that don’t depend on color.
- Example: A designer can print sample textures, fit tests, or logo keychains using leftover filament from previous prints.
- Tip: Keep a folder of simple STL models (like brackets, cable clips, or mini figures) ready for moments when you need to use the last meters of filament.
These small prints are perfect for giveaways, client samples, or warm-up tests before big projects. Instead of wasting material, you gain experience — and possibly customer engagement.
2. Combine Colors and Materials Creatively
Another clever way to stretch your 3D filament is by combining leftovers of different colors within one project. With a bit of planning, you can create beautiful artistic effects, like natural gradients or multicolor textures.
Many makers even sell these “multi-filament” pieces as exclusive items. The key is ensuring that the materials match — for example, only mixing PLA with PLA — and adjusting the temperature accordingly. Mismatched materials can ruin a print or damage your nozzle.
If you sell online, highlight this as a sustainable practice: “Each piece is made with recycled filament sections — unique, colorful, and eco-conscious.” It’s a great way to turn recycling into branding.
3. Use Leftovers for Calibration, Leveling, and Supports
Before every major print, it’s common to test the first layer, flow rate, or temperature. Instead of wasting new material, use old 3D filament scraps for calibration and support structures. They don’t need to look perfect — they just need to work.
Using up leftover filament for test prints keeps your premium materials for important projects while minimizing environmental impact. Every successful calibration using scraps equals less waste overall.
Pro tip: Keep a small “testing kit” with short lengths of different filaments labeled by brand and ideal temperature. It’ll save time and ensure consistent results whenever you start a new project.
4. The Hidden Enemy: Humidity and Poor Storage
Humidity is one of the biggest threats to 3D filament quality. Even materials like PLA, considered more stable, can absorb moisture from the air. When this happens, the filament becomes brittle, forms bubbles during extrusion, and creates rough or weak prints. PETG, ABS, and Nylon are even more sensitive — with performance drops of up to 30% if improperly stored.
How Humidity Damages 3D Filament
When wet filament is heated, trapped water vaporizes inside the nozzle, creating microbubbles that ruin the print surface. The result? Stringy, weak, and inconsistent layers that fail mechanical stress tests.
- Signs of wet filament: popping sounds during printing, uneven extrusion, dull surface finish, and visible hairlike strings.
- Most affected materials: Nylon, PETG, PVA, and TPU.
Community tests show that humidity can lower tensile strength by 40% and reduce adhesion between layers — especially in warm, humid climates.
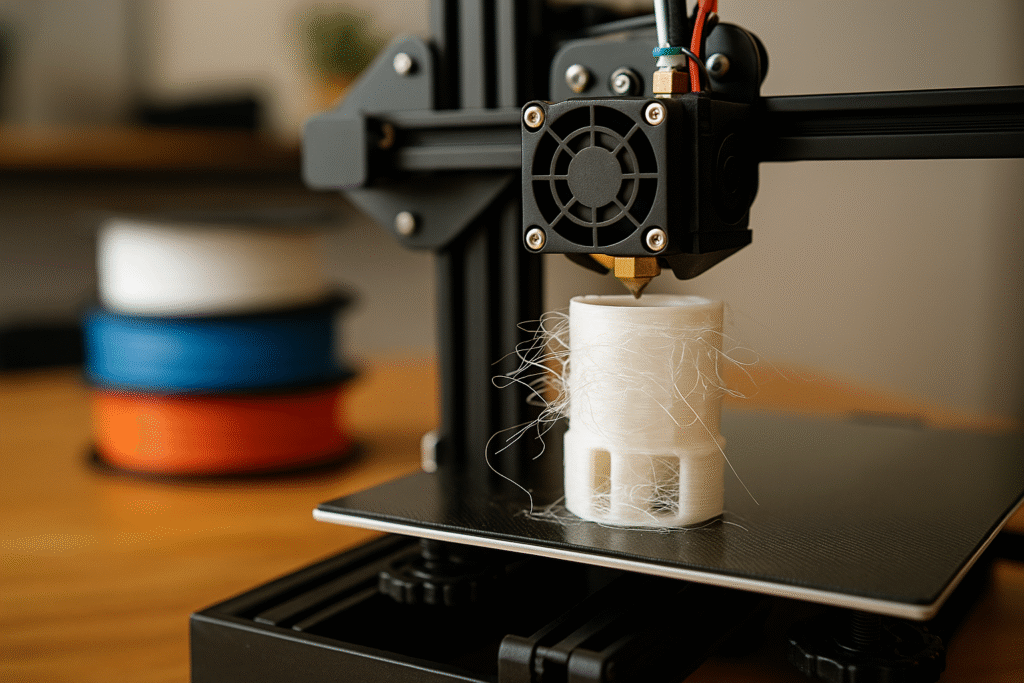

5. Storing and Reviving Your 3D Filament
Good storage habits make a huge difference in your 3D filament longevity. Luckily, you don’t need expensive equipment — just consistency and a few smart tools.
- Airtight boxes: Store your spools in sealed plastic containers with silica gel packs to absorb moisture.
- Reusable desiccants: Get color-changing desiccant packs that indicate when they’re full of humidity and ready to be recharged.
- Filament dryers: Many modern printers and third-party brands sell affordable filament dryers that maintain a constant temperature (around 50 °C) and can feed the filament directly into the printer.
How to Dry Wet Filament
If your filament already absorbed moisture, don’t panic. You can dry it safely in an electric oven at 50 °C–60 °C for 4–6 hours, depending on the material type. Dedicated filament dryers are safer and more efficient for regular users.
Warning: Never use a microwave! It can cause uneven heating and damage both the filament and your oven.
6. Recycled and Eco-Friendly Filament: A New Market
Sustainability is reshaping the 3D filament industry. Many manufacturers now collect plastic waste or old filament spools to produce new recycled filament rolls. These are often cheaper and just as reliable as standard materials.
There’s also a growing DIY trend — home extruders like Filabot or Recreator 3D let you grind your leftover prints and turn them back into usable filament. While the upfront cost is higher, long-term savings and environmental benefits make it worth considering.
Recycled filament adds a storytelling element to your work: “This model was printed using recycled PLA from previous prototypes.” Consumers love authenticity and sustainable practices — and 3D printing is the perfect field for both.
7. Minimize Waste During Filament Changes
Filament changes can lead to a surprising amount of waste. But modern slicers now include smart color change features that minimize material purging. Instead of discarding long lengths of filament, print small calibration models or decorative clips during the transition.
Some slicers (like Cura, Bambu Studio, and PrusaSlicer) even have built-in color transition towers that optimize extrusion. This technique reduces waste while ensuring smooth color blending across layers.
Tip: Keep a folder of “transition models” ready — simple designs you can print whenever you switch colors. These models serve as purge objects and small giveaways at the same time.
8. Temperature Calibration and Filament Optimization
Every type of 3D filament behaves differently under heat. Printing at the wrong temperature can waste entire spools. Too hot — and you’ll see stringing, blobs, and rough textures. Too cold — and you’ll get poor adhesion and weak layers.
That’s why it’s essential to print temperature towers every time you try a new brand or filament type. These tests use minimal material but help find the perfect printing temperature for optimal strength and quality.
Document your best settings in a notebook or spreadsheet. Knowing your ideal printing range for each filament will prevent failed prints and unnecessary waste in the future.
9. Join Filament Swap Communities
If you have leftover bits too small for new prints, consider trading them with others in the maker community. Filament swap groups on Reddit, Facebook, and Discord allow creators to exchange partial spools, test new colors, or try different materials without extra cost.
This not only saves money but also fosters collaboration and friendship among makers. Sharing knowledge and material keeps the 3D printing world vibrant and sustainable — proving that innovation grows stronger when shared.
Conclusion: Every Gram Matters
Keeping your 3D filament under control isn’t just about saving money — it’s about adopting a smarter, more sustainable mindset. With a few changes in your routine — planning color swaps, drying your spools, reusing leftovers — you can cut costs by up to 25% and dramatically improve print quality.
👉 Want more tips on sustainable 3D printing and filament optimization? Check out our other articles on TechInNess (How to Make Money with 3D Printing Without Having a Printer at Home) and subscribe to our newsletter to get access to our free PDFs with guides and ideas for creative makers!
Frequently Asked Questions
- How should I store 3D filament?
Use airtight containers with silica gel and keep spools away from sunlight and humidity. - Can I reuse short pieces of filament?
Yes! Use filament joiners or small prints to make the most of them. - What happens if my filament gets wet?
It produces bubbles, weak layers, and rough finishes. Always dry it before printing again. - Is recycled filament worth buying?
Definitely — it’s cheaper, eco-friendly, and offers comparable quality for most applications. - Which software helps save filament?
Cura, PrusaSlicer, and Bambu Studio all feature filament-saving and optimization tools. - How can I tell if my filament has gone bad?
Listen for popping sounds, check flexibility and shine — brittle or matte filaments likely absorbed moisture.